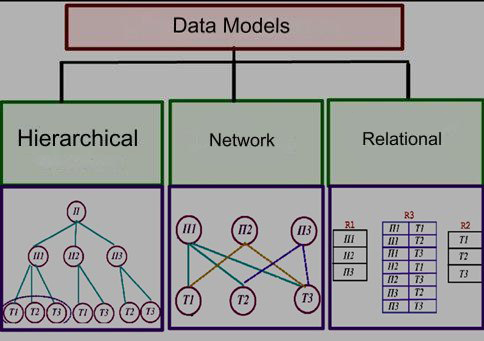
Data model is a way of organizing the logical structure of data storage in a database. There are three main types of data models which differ by the way of establishing links between the data.
- Hierarchical:
- the information is organized in accordance with the tree structure principle, in the form of “ancestor-descendant” relations;
- each record can have no more than one parent record and several subordinate records;
- graphically it can be represented as an inverted tree consisting of objects of different levels, where the vertices are the information units and the arcs are the links;
- there is a single entry point; it is impossible to implement “many-to-many” relations;
- an example of such a model is the Windows Folder Catalogue.
- Network:
- represents data as a graph-like network structure;
- any object can be connected with any quantity of the other elements;
- there are several entry points;
- graphically it can be represented as an oriented graph consisting of nodes (vertices) and links (edges) between nodes, each node can have multiple links to other nodes;
- Relational:
- it is oriented on the data organization in the form of two-dimensional tables (relations), where a table is a regular structure, it consists of similar rows divided into the columns (attributes);
- each row of a table must have a unique identifier called primary key;
- normalization of the data is obligatory for the tables – minimization of the number of repeated data;
- the distinctive feature of this model is the simplicity of data placement and ease of its interpretation;
- it is the basis of most modern DBMSs.
As far as the other models are concerned, I will describe them in the upcoming posts, so stay tuned!